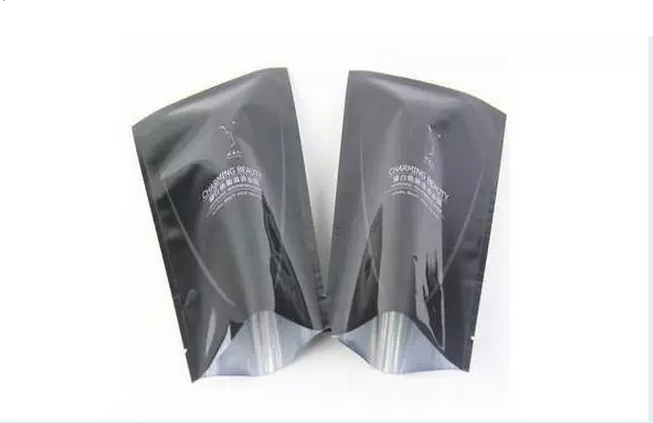
Production Requirements for Stand-up Spout Bags
Release Date:
2022-01-12
The stand-up spout bag consists of two parts: the spout and the stand-up bag. It is a type of soft packaging bag with a horizontal support structure at the bottom and a spout at the top or side. Its production requires high standards; if not properly controlled, defective products may result, leading to issues such as bag inflation, bag breakage, and leakage during use. The production of stand-up spout packaging bags mainly involves several steps: design, plate making, printing, lamination, curing, slitting, and bag making. In this issue, we will focus on the key points to note in lamination and bag making. 1. Selection of Lamination Materials 1. Outer layer: The outer layer is the substrate material. Commonly used substrate materials for stand-up bags in the market, besides ordinary OPP for slitting, include high-strength, high-barrier materials such as PET and PA. For packaging solid products like dried fruits, ordinary materials such as BOPP and matte BOPP can be used; for packaging liquids, PET or PA materials are generally selected. 2. Middle layer: The middle layer is generally chosen for its high strength and high barrier properties. Additionally, the surface tension of the middle layer material must meet lamination requirements and have good affinity with the adhesive. Therefore, materials such as PET, PA, VMPET, and aluminum foil are commonly used. 3. Inner layer: The inner layer is the heat-sealing layer, typically made of PE, CPE, CPP, or other materials with strong low-temperature heat-sealing performance. The surface tension of the laminated side must meet lamination requirements, but the heat-sealing surface tension must be below 34 mN/m and possess good anti-contamination, anti-static, and heat-sealing properties. 2. Requirements for Bag Making Process 1. Heat-sealing temperature: When setting the heat-sealing temperature, factors to consider include the characteristics of the heat-sealing material, film thickness, the number of heat-sealing presses, and the size of the heat-sealing area. Generally, if the same area is pressed multiple times, the heat-sealing temperature can be set slightly lower. 2. Heat-sealing pressure: Appropriate pressure must be applied during heat sealing to promote adhesion of the heat-sealing materials. However, the pressure must be controlled carefully; excessive pressure can cause molten material to be squeezed out, affecting the flatness of the bag and the heat-sealing effect, thereby reducing heat-sealing strength. 3. Heating method: The heating method of the heat-sealing knife during bag making can be divided into single-sided heating and double-sided heating. Double-sided heating is more efficient and practical than single-sided heating. The main issues encountered in the actual production of stand-up spout bags lie in these two aspects. Therefore, how to select materials properly and adopt the best process operation methods plays a decisive role in improving the overall quality of stand-up spout bags.


Keywords:
Next
Next:
Recommended News
Shantou Jinlei Plastics Industrial Co., Ltd.
Phone: 086-754-82511088 / 82511033
Mobile: 8613902732666
Address: 1st and 3rd Floors, Rear Building, Factory No. 35 Shengye Road, Jinping District, Shantou City, Guangdong Province
Email: jl@stjinlei.com

Scan with Mobile
Copyright © Jinlei Plastics